The proportion of people with immigrant backgrounds has increased in Sweden over time (See more in Immigration in Sweden I). How is it by region and municipality? In Sweden, there are 21 regions and 290 municipalities. There may be regional differences in terms of the proportion of people with immigrant backgrounds. Figure 1a-b shows the proportion of Swedish natives and people with immigrant backgrounds in 21 regions from 2002 to 2023.
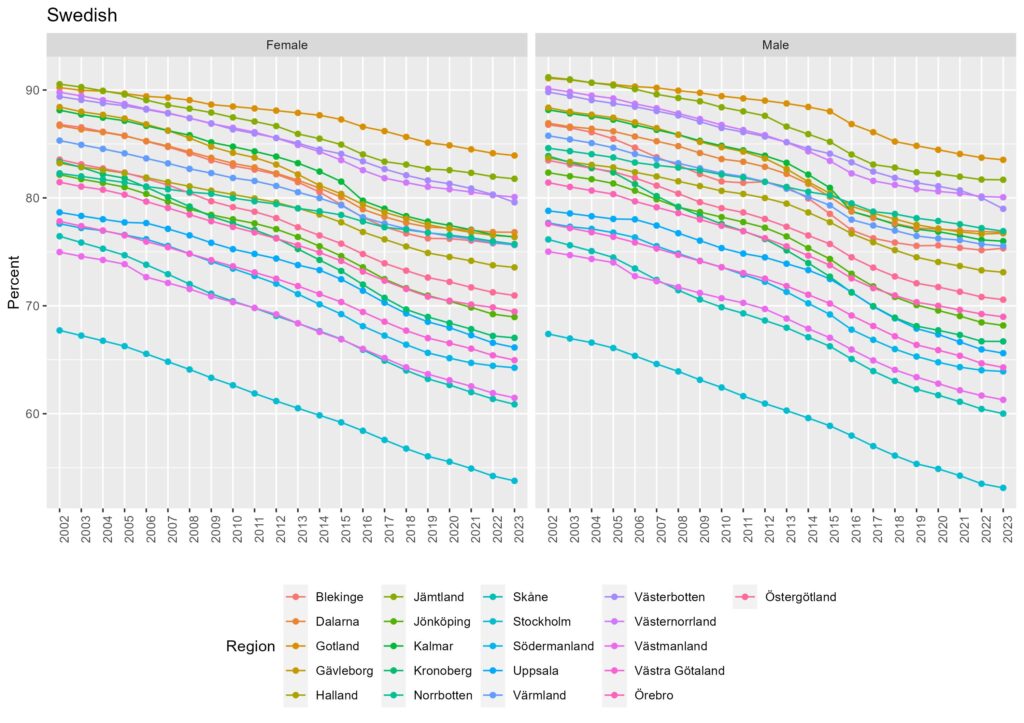
From Figure 1a-b, the proportion of the Swedish native population has decreased due to the increase in people with immigrant backgrounds over 20 years across all regions. However, there are regional differences. For example, the top 3 regions with the highest proportion of people with immigrant backgrounds are Stockholm, Skåne, and Västra Götaland, where the 3 largest cities in Sweden; Stockholm, Malmö, and Göteborg are located. On the other hand, the proportion of Swedish native population remained above 80 % in Gotland, Jämtland, Västernorrland, and Västerbotten regions, where the population is low and located rather north of Sweden.
When we look into those regions by municipality, we can see differences in the municipality levels.
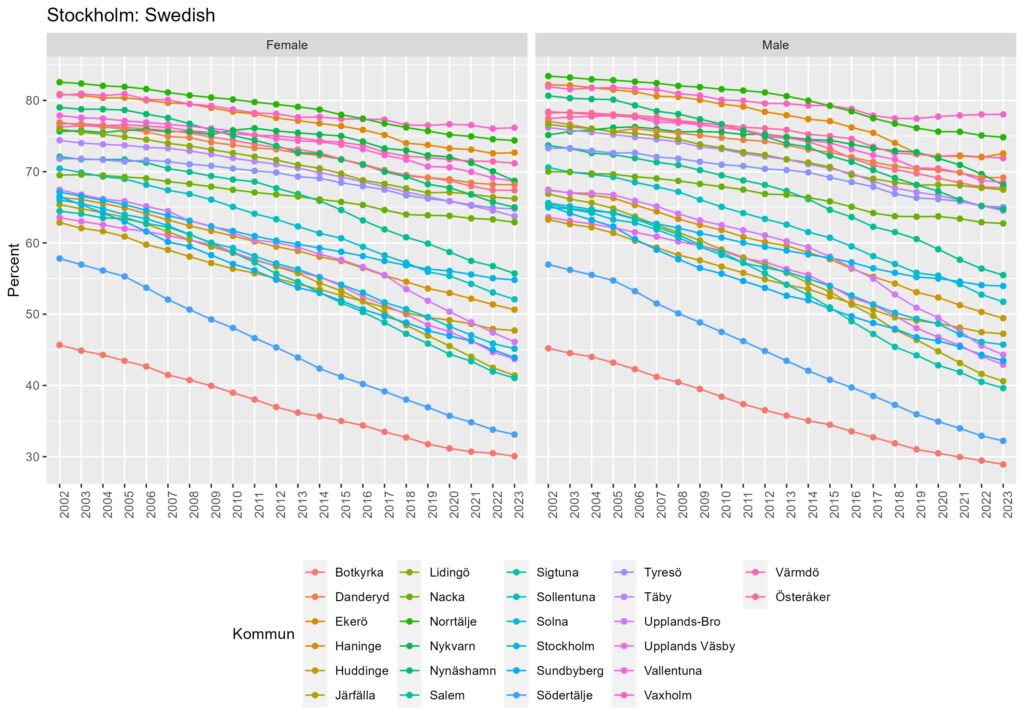
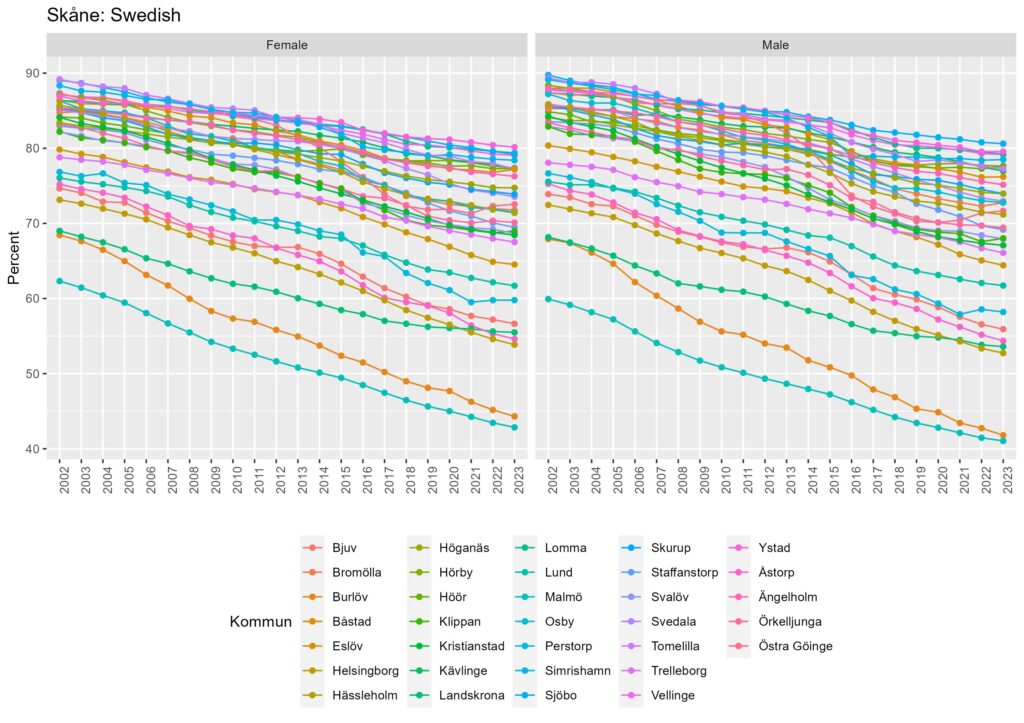
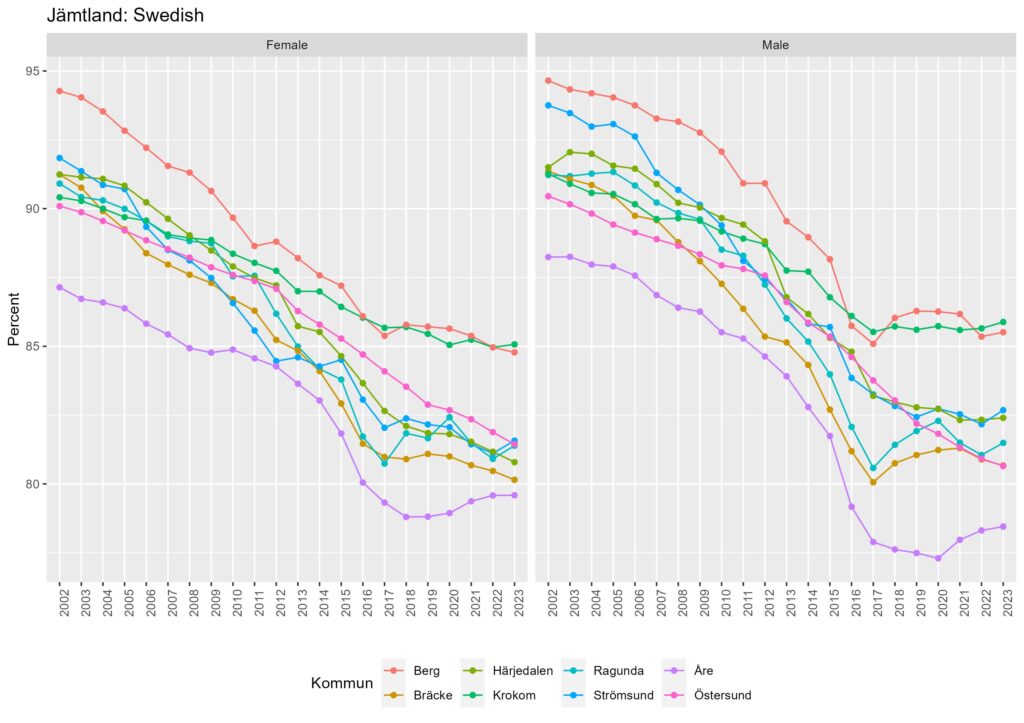
From Figure 2a-c, we can see that the proportion of Swedish natives has decreased across all municipalities in Stockholm, Skåne, and Jämtland. Still, the degree of decrease is different by municipalities in each region. In some municipalities, the proportion of Swedish natives remained high even though it has decreased over time.
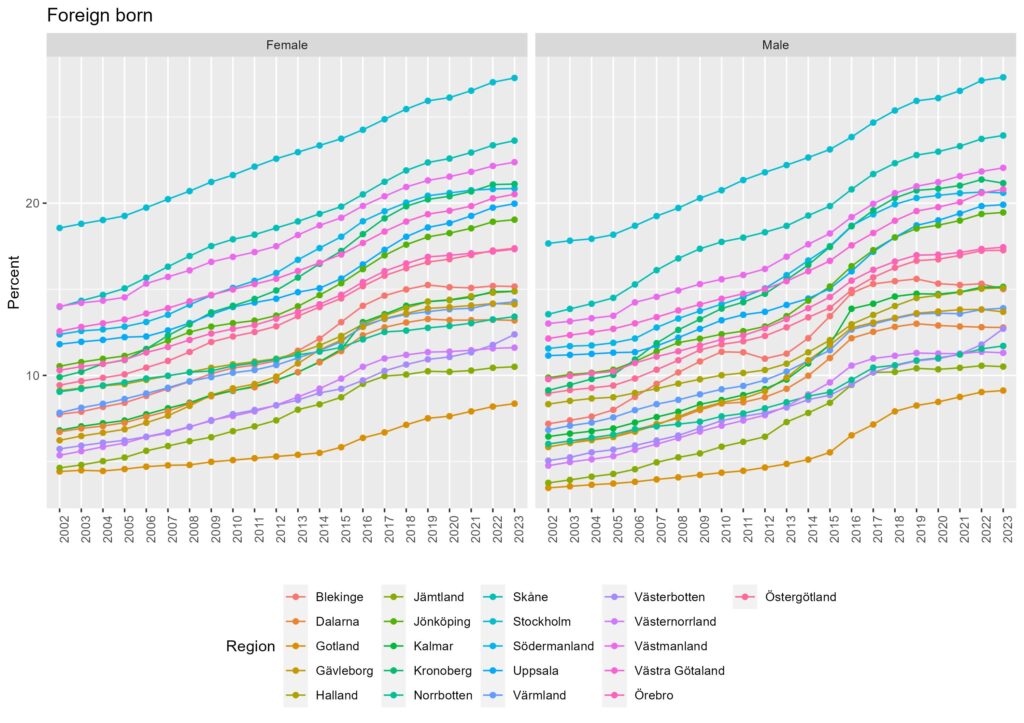
Visualizing those on the map for the regional variation of native/immigrant population composition over time would give us further insight. Figure 3 shows the proportion of people who were born outside of Sweden in each 21 regions from 2002 to 2023. While it has increased across all regions, it is more conspicuous in southern regions.
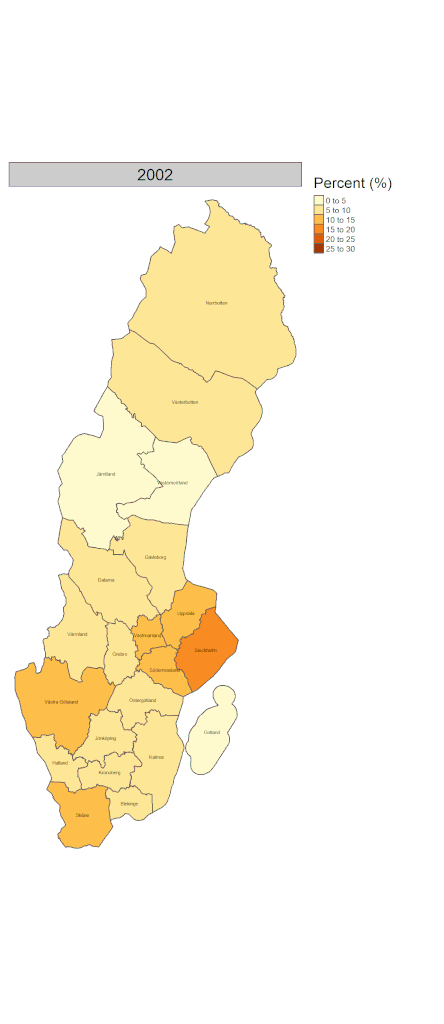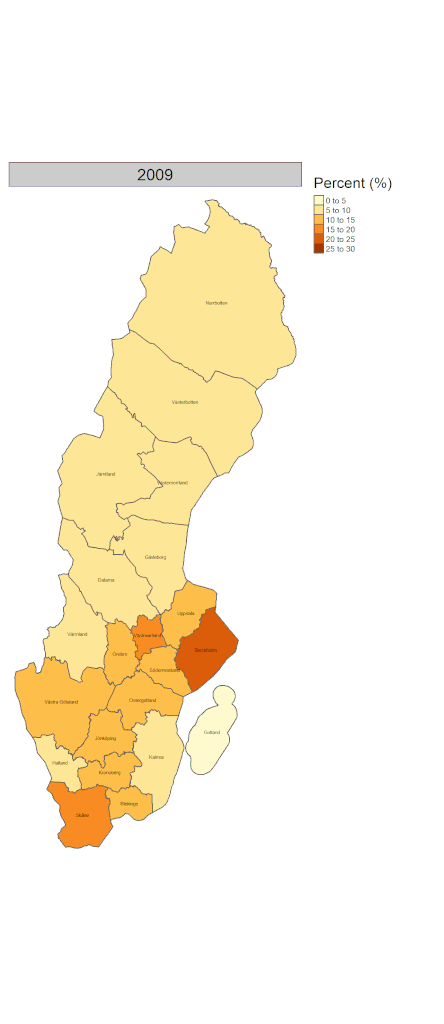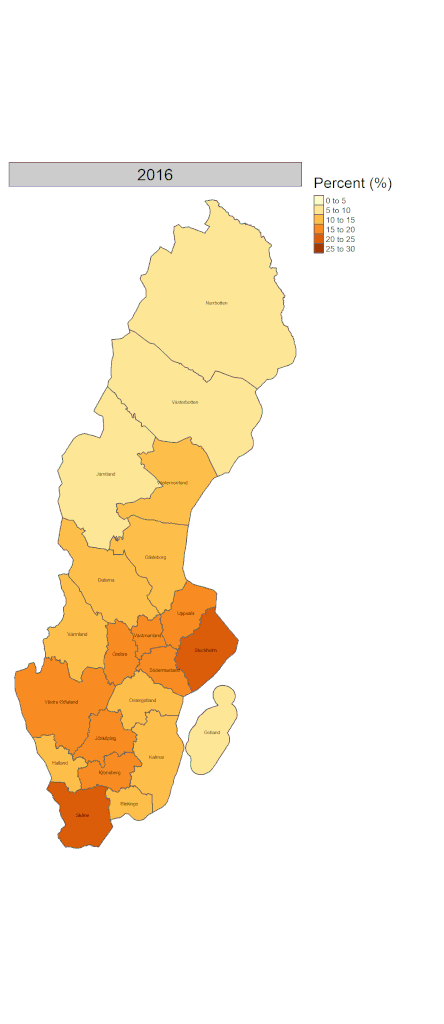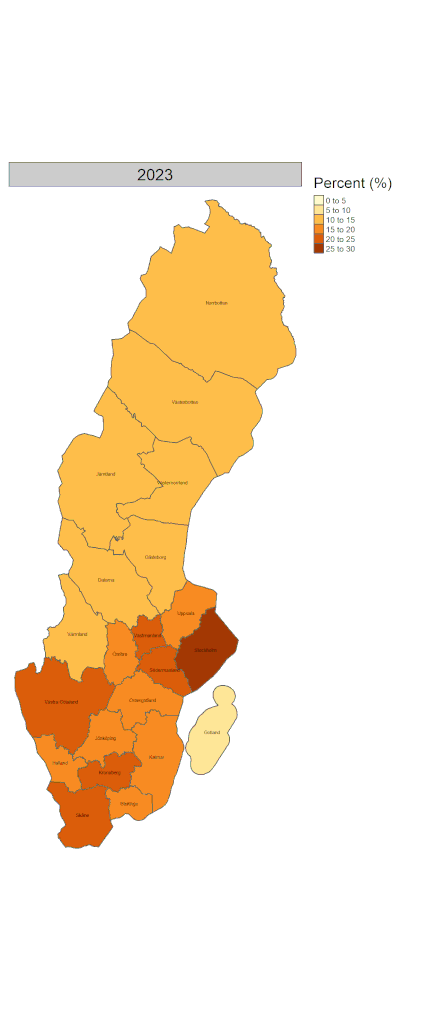
The differences in the proportion of immigrants within regions and municipalities indicate the increased segregation of immigrants. It is, in general, easier for both host societies and immigrants themselves to settle in the places where migrant density is high. There are both pros and cons for immigrants to live in areas where there are many migrants from the same country. However, evidence shows that integration into the mainstream of society may be hampered or delayed by living in such areas (2). This can be said of rural areas where migrant density tends to be low and local residents may keep traditional lifestyles and cultures. More research is needed on how these are associated with the health outcomes of migrants.
References
- Statistics Sweden. Statistiska Centralbyrån. 2023 [cited 2024 Feb 7]. Population. Available from: https://www.scb.se/en/finding-statistics/statistics-by-subject-area/population/
- World Health Organization. (2023). Mental health of refugees and migrants: risk and protective factors and access to care. World Health Organization.
